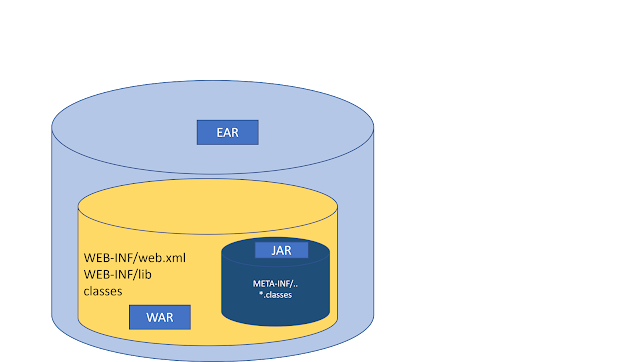
J2EE defines three types of archives:
- EAR
- WAR
- JAR
When Java applications are deployed, all of the files that constitute
the Java app are compressed and packaged into a single file. While compressed
files are typically given a .zip extension, the Java community instead uses
.ear, .war and .jar files.
Under the hood, EAR, JAR and WAR files are all simply zip files that contain the various images, XML files, property files and pieces of Java code that make up a Java application.
- Java
Archive (JAR) A
JAR file encapsulates one or more Java classes, a manifest, and a
descriptor. It also holds generic libraries of
Java classes, resources, auxiliary files.
- JAR files are the lowest
level of archive. JAR files are used in J2EE for packaging EJBs and client-side
Java Applications.
- Actually, jar file contains all the .class files of our java
project.
Extension- .jar
- Web
Archive (WAR) A
WAR files are similar to JAR files, except that they are specifically for
web applications made from Servlets, JSPs, and supporting classes. These
are intended to contain complete Web applications. Web
application contain all the web related Technologies like Html,Css,
Javascript , Jsp,Servlet ,Xml etc and War file is a compressed form of web
application which allows us to make that application portable. Struts and Spring based Web
applications may be archived to a WAR.
·
Extension- .war
- Enterprise Archive (EAR) An EAR file contains all
of the components that make up a particular J2EE application. are
intended to contain complete enterprise applications. In this context, an
enterprise application is defined as a collection of .jar files,
resources, classes, and multiple Web applications. An EAR
may contain one or more WAR files. EAR files can also contain connector
modules packaged as RAR files and Client modules packaged as JAR
files.
·
Extension- .ear
Summary:
An
EAR file requires a fully Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE)- or
Jakarta Enterprise Edition (EE)-compliant application server, such as WebSphere or JBoss, to run.
A WAR file only requires a Java EE Web
Profile-compliant application server to run.
A JAR file only requires a Java installation.



No comments:
Post a Comment